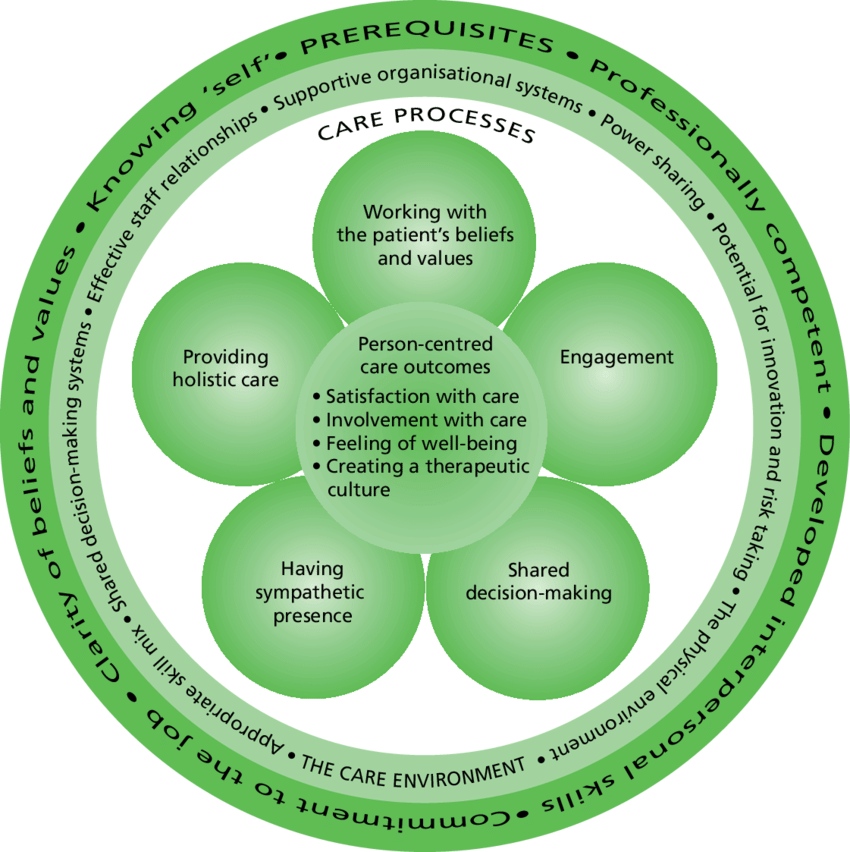
In the realm of healthcare, providing effective and compassionate care goes beyond medical expertise. It requires a shift in focus from a provider-centric model to a patient-centered approach, where patients’ needs, preferences, and experiences are prioritized. A patient-centered health care approach recognizes that patients are not just passive recipients of care but active participants in their own well-being. This blog will delve into the concept of patient-centered health care, explore its benefits, discuss strategies for implementation, examine tools and technologies that enhance patient-centered care, and address the challenges and barriers that may arise.
Understanding Patient-Centered Health Care
At its core, patient-centered health care places patients at the center of their care journey. It is an approach that acknowledges and respects patients’ autonomy, values, and individual circumstances. The primary goal is to improve health outcomes and enhance patient satisfaction. Key principles of patient-centered care include active patient engagement, shared decision-making, and personalized care plans. By involving patients in their care, healthcare providers can tailor treatments to their specific needs, ensuring a more holistic and effective approach.
Benefits of a Patient-Centered Approach
Adopting a patient-centered approach yields numerous benefits for both patients and healthcare systems. Firstly, it has a positive impact on health outcomes. When patients are actively engaged in their care, they are more likely to adhere to treatment plans, leading to better overall health and well-being. Moreover, shared decision-making empowers patients to make informed choices about their treatment options, increasing treatment satisfaction and reducing the likelihood of medical errors or unnecessary interventions. Patient satisfaction plays a vital role in healthcare delivery as it contributes to improved health outcomes, increased patient loyalty, and reduced healthcare disparities.
Implementing Patient-Centered Care
To implement patient-centered care effectively, healthcare systems need to adopt strategies that promote patient engagement and communication. Effective communication between healthcare providers and patients is crucial for building trust, ensuring shared understanding, and fostering a collaborative relationship. Shared decision-making, where patients and providers work together to develop personalized care plans, enhances patient autonomy and improves treatment adherence. Additionally, care coordination and multidisciplinary approaches help integrate various healthcare services, ensuring continuity of care and a seamless patient experience.
Tools and Technologies for Enhancing Patient-Centered Care
In the digital age, technology plays a vital role in facilitating patient engagement and communication. Electronic health records (EHRs) and patient portals provide patients with access to their medical information, test results, and appointment scheduling, allowing them to actively participate in their care. These tools enable patients to communicate with their healthcare providers, ask questions, and engage in shared decision-making. Furthermore, innovative technologies like telemedicine and remote monitoring enhance access to care, particularly for individuals in remote areas or with mobility limitations, providing convenience and reducing barriers to receiving timely and appropriate care.
Overcoming Challenges and Barriers
Implementing a patient-centered approach is not without its challenges. Common barriers include resistance to change, lack of provider education, time constraints, and systemic barriers. To address these challenges, healthcare systems need to invest in comprehensive provider education, emphasizing the importance of patient-centered care and the skills necessary for its successful implementation. Cultural competency training can also help healthcare providers understand and address the diverse needs and preferences of patients from different backgrounds. System-wide policy changes should be implemented to support and incentivize patient-centered care, while continuous feedback and quality improvement initiatives can drive ongoing refinement and optimization.
Conclusion:
A patient-centered health care approach is essential for delivering high-quality, personalized care that improves health outcomes and enhances patient satisfaction. By placing patients at the heart of care, healthcare providers and systems can foster a collaborative relationship that empowers patients, respects their autonomy, and tailors treatments to their specific needs. Implementing effective communication, shared decision-making, care coordination, and leveraging technology are vital components of a patient-centered approach. While challenges may arise, a commitment from healthcare providers, policymakers, and patients themselves is crucial in fostering a patient-centered approach and creating a healthcare system that prioritizes patients’ needs, preferences, and experiences. Ultimately, patient-centered care has the potential to transform healthcare delivery and improve the well-being of individuals and communities alike.